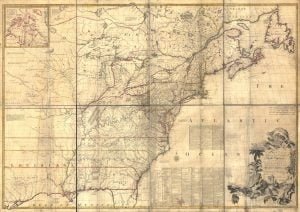
John Mitchell’s Map
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were directly used to help establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the Treaty of Paris (1783) that ended the American Revolutionary War. The map’s inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine. Its supposition that the Mississippi extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that … Read more