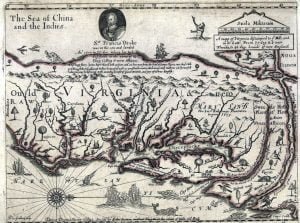
The Archaeological Evidence in Shenandoah Valley
Native American artifacts are frequently found in the Seven Bends area of the Shenandoah River between Woodstock and Strasburg, VA. However, mounds and earthworks are mostly concentrated in the bends near the outlet of Toms Brook at Maurertown, VA. The mounds were fairly prominent when settlers first arrived, but after 250 years of plowing, they generally can only be found in aerial photographs. Paleo-Indian Period Warren County During the 1990s, the Thunderbird Archaeological District was surveyed and partially excavated. Thunderbird consists of three sites that were occupied or utilized during the Paleo-Indian and Early Archaic Periods. It was the first … Read more