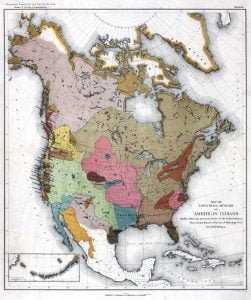
Linguistic Families of American Indians North of Mexico
The Powell map of “Linguistic Families of American Indians North of Mexico,” first published in 1891, has been a valuable resource for understanding the diverse linguistic groups of Native American tribes. Despite its utility, there has been a need for a detailed map showing the specific locations of tribes within these families. This article addresses that gap by exploring the complexities of defining and mapping tribes, particularly given the non-uniform application of the term “tribe” and the varying levels of coherence among different groups. The article emphasizes the challenges in creating such a map, especially when considering the historical movements and interactions of these tribes.